نیزاتیدین
محلول دهانی اکسید
نام عمومی: نیازاتیدین
فرم دوز: محلول خوراکی
- بارداری
در این صفحه
- توضیحات
- فارماکولوژی بالینی
- موارد مصرف و استفاده از آن
- موارد منع مصرف
- موارد احتیاطی
- تداخلات دارویی
- واکنشهای جانبی / عوارض جانبی
- مصرف بیش از حد دارو
- مقدار و نحوه مصرف
- نحوه تهیه / ذخیره سازی و نحوه مدیریت
نام تجاری Axid Oral Solution در ایالات متحده متوقف شده است اگر نسخه های عمومی این محصول توسط FDA تأیید شده باشد ، ممکن است معادل های عمومی در دسترس باشد .
شرح
نازاتیدین (USP) یک آنتاگونیست گیرنده H 2 هیستامین است. از نظر شیمیایی ، N- [2 – [[[2 – [(دی متیل آمینو) متیل] -4-تیازولیل] متیل] تیو] اتیل] -N “-متیل -2 است. -nitro-1،1-ethenediamine.
فرمول ساختاری به شرح زیر است:
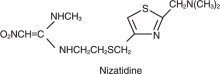
نازاتیدین فرمول تجربی C 12 H 21 N 5 دارد O 2 S 2 که نمایانگر وزن مولکولی 331.47 است. این ماده جامد بلوری سفید و منفرد است که در آب محلول است. نازاتیدین طعم تلخ و بویی ملایم مانند گوگرد دارد.
محلول خوراکی اکسید به عنوان یک محلول خوراکی شفاف و زرد با عطر و طعم صمغ حباب فرموله شده و هر 1 میلی لیتر حاوی 15 میلی گرم نیرازیدین است. محلول خوراکی اکسید همچنین حاوی مواد غیرفعال متیل پارابن ، پروپیل پارابن ، گلیسیرین ، سدیم آلژینات ، آب تصفیه شده ، کلرید سدیم ، سدیم ساخارین ، سدیم سدیم دی هیدرات ، اسید سیتریک بی آب ، ساکارز ، طعم آدامس حباب ، تقویت کننده شیرینی مصنوعی و هیدروکسید سدیم است.
داروسازی بالینی در بزرگسالان: نازاتیدین یک مهار کننده قابل رقابت و برگشت پذیر هیستامین در هیستامین H 2 span است > گیرنده ها ، به ویژه آنهایی که در سلول های جداری معده هستند.
فعالیت ضد ترشحی —1. تأثير بر ترشح اسيد : نيازاتيدين تا 12 ساعت به طور قابل توجهي ترشح اسيد معده شبانه را مهار مي کند. همچنین نازاتیدین به طور قابل توجهی ترشح اسید معده را که توسط غذا ، کافئین ، بتازول و پنتاگاسترین تحریک می شود ، مهار می کند ( جدول 1 ).
| زمان بعد دوز (ساعت) Ltd.> |
٪ مهار اسید معده تولید با دوز (میلی گرم) Ltd.> |
|||||
| 20-50 | 75 | 100 | 150 | 300 | ||
| شبانه بتازول پنتاگاسترین غذا کافئین Ltd.> |
حداکثر 10 حداکثر 3 تا 6 حداکثر 4 حداکثر 3 |
57 – – 41 – |
– 93 25 64 73 |
73 – – – – |
– 100 64 98 85 |
90 99 67 97 96 |
2. اثرات آن بر سایر ترشحات دستگاه گوارش – پپسین : مصرف خوراکی 75 تا 300 میلی گرم نیازاتیدین بر فعالیت پپسین در ترشحات معده تأثیری ندارد. کل تولید پپسین متناسب با کاهش حجم ترشحات معده کاهش یافت.
عامل ذاتی : تجویز خوراکی 75 تا 300 میلی گرم نیازاتیدین باعث افزایش ترشح عامل ذاتی بتازول می شود.
غلظت گاسترین سرم : نازاتیدین هیچ تاثیری بر غلظت پایه گاسترین سرم نداشت. وقتی غذا 12 ساعت پس از مصرف نیزاتیدین بلعیده شد ، هیچ ترشحی از ترشح گاسترین مشاهده نشد.
3. سایر اقدامات دارویی –
-
- هورمون ها : نشان داده نشد که نازاتیدین بر غلظت سرمی گنادوتروپین ها ، پرولاکتین ، هورمون رشد ، هورمون ضد ادرار ، کورتیزول ، تریودو تیرونین ، تیروکسین ، تستوسترون ، 5 α- تأثیر می گذارد. دی هیدرو تستوسترون ، آندروستندیون یا استرادیول.
- نازاتیدین هیچ اقدام ضد آندروژنی قابل قبولی نداشت.
4. فارماکوکینتیک – فراهمی زیستی مطلق خوراکی نیژاتیدین بیش از 70٪ است.
حداکثر غلظت پلاسما (700 تا 1800 میکروگرم در لیتر برای دوز 150 میلی گرم و 1400 تا 3600 میکروگرم در لیتر برای دوز 300 میلی گرم) از 0.5 تا 3 ساعت پس از دوز رخ می دهد. غلظت پلاسما 12 ساعت پس از مصرف کمتر از 10 میکروگرم در لیتر است. نیمه عمر حذف 1 تا 2 ساعت ، پاکسازی پلاسما 40 تا 60 لیتر در ساعت و حجم توزیع 0.8 تا 1.5 لیتر در کیلوگرم است. به دلیل نیمه عمر کوتاه و ترخیص سریع از نازاتیدین ، تجمع دارو در افرادی که عملکرد کلیوی طبیعی دارند یا 300 میلی گرم یک بار در روز قبل از خواب یا 150 میلی گرم دو بار در روز مصرف می کنند ، انتظار نمی رود. نازاتیدین نسبت دوز را در محدوده دوز توصیه شده نشان می دهد.
فراهمی زیستی خوراکی نیازاتیدین در اثر مصرف همزمان پروپانتلین آنتی کولینرژیک تأثیر ندارد. ضد اسیدهای متشکل از هیدروکسیدهای آلومینیوم و منیزیم به همراه سیمتیکون ، میزان جذب نیزاتیدین را حدود 10٪ کاهش می دهند. با غذا ، AUC و C max تقریباً 10٪ افزایش می یابد. در انسان ، کمتر از 7٪ دوز خوراکی به عنوان N2-monodesmethylnizatidine ، یک آنتاگونیست گیرنده H 2 متابولیزه می شود ، که متابولیت اصلی دفع شده از طریق ادرار است. سایر متابولیت های احتمالی اکسید N2 (کمتر از 5٪ دوز) و S-اکسید (کمتر از 6٪ دوز) هستند.
بیش از 90٪ از دوز تجویز شده خوراکی نیژاتیدین در طی 12 ساعت از طریق ادرار دفع می شود. حدود 60٪ از دوز خوراکی به عنوان داروی بدون تغییر دفع می شود. ترخیص کالا از گمرک کلیه حدود 500 میلی لیتر در دقیقه است که نشان دهنده دفع با ترشح فعال توبولی است. کمتر از 6٪ دوز تجویز شده در مدفوع از بین می رود.
نارسایی متوسط تا شدید کلیه به طور قابل توجهی نیمه عمر را افزایش می دهد و میزان ترخیص کالا از گمان نیازاتیدین را کاهش می دهد. در افرادی که از نظر عملکردی بی حس هستند ، نیمه عمر 3.5 تا 11 ساعت و ترخیص کالا از گمرک پلاسما 7 تا 14 لیتر در ساعت است. برای جلوگیری از تجمع دارو در افراد با اختلال کلیوی از نظر بالینی ، مقدار و / یا دوزهای دوزهای نیزاتیدین باید متناسب با شدت اختلال عملکرد کاهش یابد ( رجوع کنید به مقدار مصرف و تجویز ).
تقريباً 35٪ نيازاتيدين به پروتئين پلاسما متصل است ، عمدتاً به α 1 گلوكوپروتئين اسيد. وارفارین ، دیازپام ، استامینوفن ، پروپانتلین ، فنوباربیتال و پروپرانولول بر اتصال پروتئین پلاسما به نیژاتیدین در شرایط آزمایشگاهی تأثیری نداشتند.
با دوز 150 میلی گرم ، محلول خوراکی اکسید (15 میلی گرم در میلی لیتر) دو برابر با کپسول های نیژاتیدین است.
فارماکولوژی بالینی در بیماران کودکان:
فارماکوکینتیک
جدول 2 داده های فارماكوكینتیكی نیزاتیدین را كه به صورت خوراكی در نوجوانان مبتلا به ریفلاك معده (GER) و بزرگسالان سالم تجویز می شود ، ارائه می دهد. پارامترهای فارماکوکینتیک برای بیماران نوجوان 12 تا 18 ساله با پارامترهای بزرگسالان قابل مقایسه است.
|
SD = تک دوز SS = حالت ثابت |
||||||||
|
تجویز کپسول های نیزاتیدین در آب سیب منجر به کاهش 27 درصدی فراهمی زیستی نیازاتیدین می شود. |
||||||||
| محدوده سن | فرمول | دوز | C حداکثر (ng / mL) |
T حداکثر (ساعت) |
AUC 0 – ∞ (ng • h / mL) |
CL F (L / h) |
Vd F (L) |
T 1/2 (ساعت) |
| 12-18 سال | کپسول | 150 میلی گرم SD | 1422.9 | 1.3 | 3764.2 | 41.0 | 71.4 | 1.2 |
| نوجوانان | 150 میلی گرم SS | 1480.2 | 1.4 | 3776.1 | 41.1 | 74.2 | 1.3 | |
| با GER | ||||||||
| سالم | کپسول | 150 میلی گرم SD | 1367.6 | 1.0 | 3703.1 | 41.9 | 83.4 | 1.4 |
| بزرگسالان | راه حل دهان | 150 میلی گرم SD | 1340.6 | 0.8 | 3610.9 | 43.0 | 86.4 | 1.4 |
| آب سیب | 150 میلی گرم SD | 762.8 | 1.3 | 2694.1 | 57.5 | 142.3 | 1.7 | |
فارماکودینامیک
فارماكوديناميك نيازاتيدين در 48 بيمار كودكان بررسي شد. این داده ها حاکی از آن است که سرکوب اسید معده مشابه آنچه در مطالعات بزرگسالان مشاهده شده است ( جدول 3 ).
| سن | ٪ Time pH> 3 |
٪ Time PH> 4 |
AUEC 0-12h (pH • ساعت) |
| 12-18 سال | 57 | 42 | 41.4 |
| بزرگسالان | 31 | 19 | 34.8 |
آزمایشات بالینی (بزرگسالان) —1. زخم فعال اثنی عشر : در مطالعات چند مرکزی ، دوسوکور و کنترل شده با دارونما در ایالات متحده ، زخم های اثنی عشر با تشخیص آندوسکوپی با تزریق نیژاتیدین ، 300 میلی گرم در ساعت ، با سرعت بیشتری بهبود یافت. یا 150 میلی گرم در مقایسه با دارونما ( جدول 4 ). دوزهای پایین تر ، مانند 100 میلی گرم ساعت ، کمی تأثیر کمتری داشتند.
|
* P |
† P |
|||||
| نازاتیدین | دارونما |
|||||
| 300 میلی گرم ساعت | 150 mg b.i.d. | |||||
| شماره وارد شده |
بهبود یافته / قابل ارزیابی |
شماره وارد شده |
بهبود یافته / قابل ارزیابی |
شماره وارد شده |
بهبود یافته / قابل ارزیابی |
|
| مطالعه 1 | ||||||
| هفته 2 | 276 | 93/265 (35٪) * | 279 | 55/260 (21٪) | ||
| هفته 4 | 198/259 (76٪) * | 95/243 (39٪) | ||||
| مطالعه 2 | ||||||
| هفته 2 | 108 | 24/103 (23٪) * | 106 | 27/101 (27٪) * | 101 | 9/93 (10٪) |
| هفته 4 | 65/97 (67٪) * | 66/97 (68٪) * | 24/84 (29٪) | |||
| مطالعه 3 | ||||||
| هفته 2 | 92 | 22/90 (24٪) † | 98 | 13/92 (14٪) | ||
| هفته 4 | 52/85 (61٪) * | 29/88 (33٪) | ||||
| هفته 8 | 68/83 (82٪) * | 39/79 (49٪) | ||||
2. نگهداری زخم دوازدهه بهبود یافته : نشان داده شده است كه درمان با دوز كاهش یافته ای نازاتیدین به عنوان درمان نگهدارنده پس از بهبودی زخم اثنی عشر مثر است. در مطالعات چند مرکز ، دوسوکور و کنترل شده با پلاسبو که در ایالات متحده انجام شده است ، 150 میلی گرم نیازاتیدین مصرف شده هنگام خواب منجر به بروز قابل توجهی پایین تر از عود زخم اثنی عشر در بیماران تحت درمان تا 1 سال است ( جدول 5 ).
|
* P |
||
| ماه | نازاتیدین ، 150 میلی گرم ساعت | دارونما |
| 3 | 13٪ (28/208) * | 40٪ (82/204) |
| 6 | 24٪ (45/188) * | 57٪ (106/187) |
| 12 | 34٪ (57/166) * | 64٪ (112/175) |
3. بیماری ریفلاکس معده (GERD) : در 2 آزمایش بالینی چند مرکز ، دوسوکور و کنترل دارونما که در ایالات متحده و کانادا انجام شد ، نیزاتیدین نسبت به دارونما در بهبود تشخیص آندوسکوپی موثرتر بود ازوفاژیت و در بهبود ازوفاژیت فرسایشی و زخمی.
در بیماران مبتلا به ازوفاژیت فرسایشی یا اولسراتیو ، 150 میلی گرم در میلی گرم. میزان نازاتیدین داده شده به 88 بیمار در مقایسه با دارونما در 98 بیمار در مطالعه 1 میزان بهبودی بالاتری را در 3 هفته (16٪ در مقابل 7٪) و در 6 هفته (32٪ در مقابل 16٪ ، P به همراه داشت) P P
علاوه بر این ، تسکین سوزش معده همراه در بیماران تحت درمان با نیازاتیدین بیشتر بود. بیماران تحت درمان با نازاتیدین نسبت به بیمارانی که با دارونما تحت درمان قرار گرفته اند از نظر ضد اسید کمتر مصرف کرده اند.
4. زخم فعال خوش خیم معده : در یک مطالعه چند مرکزی ، دوسوکور و کنترل شده با دارونما که در ایالات متحده و کانادا انجام شد ، پس از تجویز نیازاتیدین ، زخم های خوش خیم معده با تشخیص آندوسکوپی با سرعت بیشتری بهبود یافتند. نسبت به دارونما ( جدول 6 ).
|
* مقادیر P یک طرفه است که با استفاده از آزمون مجذور کای بدست می آید و برای مقایسه های متعدد تنظیم نمی شود. |
|||
| هفته | درمان Ltd.> | نرخ بهبود Ltd.> | در مقابل. دارونما مقدار P * |
| 4 | نازاتیدین 300 میلی گرم ساعت. | 52/153 (34٪) | 0.342 |
| نيازاتيدين 150 ميلي گرم b.i.d. | 65/151 (43٪) | 0.022 | |
| دارونما | 48/151 (32٪) | ||
| 8 | نازاتیدین 300 میلی گرم ساعت. | 99/153 (65٪) | 0.011 |
| نيازاتيدين 150 ميلي گرم b.i.d. | 105/151 (70٪) | ||
| دارونما | 78/151 (52٪) | ||
در یک مطالعه چند مرکزی ، دوسوکور و کنترل شده توسط مقایسه کننده در اروپا ، نرخ بهبودی برای بیمارانی که نیژاتیدین دریافت می کنند (پیشنهاد 300 میلی گرم در ساعت یا 150 میلی گرم) معادل نرخ بیمارانی است که داروی مقایسه ای دریافت می کنند و از نظر آماری بالاتر از دارونما تاریخی است. نرخ ها را کنترل کنید.
موارد مصرف و استفاده
محلول دهان و دندان اکسید برای درمان زخم اثنی عشر تا 8 هفته نشان داده شده است. در بیشتر بیماران ، زخم ظرف 4 هفته بهبود می یابد.
محلول خوراکی اکسید برای درمان نگهدارنده برای بیماران مبتلا به زخم اثنی عشر در دوز کاهش یافته 150 میلی گرم ساعت نشان داده شده است. پس از بهبودی زخم اثنی عشر فعال. عواقب درمان مداوم با نیازاتیدین برای بیش از 1 سال مشخص نیست.
محلول خوراکی اکسید تا 12 هفته برای درمان ازوفاژیت تشخیص داده شده از طریق آندوسکوپیک ، از جمله ازوفاژیت فرسایشی و اولسراتیو و سوزش معده ناشی از ریفلاکس تجویز می شود.
محلول خوراکی اکسید تا 8 هفته برای درمان زخم خوش خیم معده نشان داده شده است. قبل از شروع درمان ، باید مراقبت شود تا احتمال زخم بدخیم معده را کنار بگذارید.
در بیماران کودکان ، محلول خوراکی Axid برای سنین 12 سال به بالا نشان داده شده است. محلول خوراکی اکسید تا 8 هفته برای درمان ازوفاژیت تشخیص داده شده از طریق آندوسکوپیک ، از جمله مری ، فرسایش و زخم و سوزش معده همراه با GERD نشان داده شده است.
موارد منع مصرف
محلول خوراکی اکسید در بیمارانی که حساسیت بالایی به دارو دارند شناخته شده است. از آنجا که حساسیت متقابل در این گروه از ترکیبات مشاهده شده است ، نباید آنتاگونیست های گیرنده H 2 ، از جمله نیزاتیدین ، در بیمارانی که سابقه حساسیت بیش از حد دیگر به H 2 .
موارد احتیاطی
عمومی —1. پاسخ علامتي به درمان نيازاتيدين مانع از وجود بدخيمي معده نمي شود.
2. از آنجا که نیزاتیدین به طور عمده از طریق کلیه دفع می شود ، دوز مصرفی باید در بیماران با نارسایی کلیوی متوسط تا شدید کاهش یابد (به مقدار مصرف و تجویز مراجعه کنید).
3. مطالعات فارماکوکینتیک در بیماران مبتلا به سندرم هپاتورنال انجام نشده است. بخشی از دوز نیزاتیدین در کبد متابولیزه می شود. در بیمارانی که عملکرد کلیوی طبیعی دارند و اختلال عملکرد کبدی بدون عارضه دارند ، میزان دفع نیروزیدیدین مشابه موارد طبیعی است.
تست های آزمایشگاهی – تست های نادرست مثبت برای urobilinogen با Multistix ® ممکن است در طول درمان با نیازاتیدین رخ دهد .
تداخلات دارویی – هیچ فعل و انفعالی بین نیازاتیدین و تئوفیلین ، کلردیازپوکساید ، لورازپام ، لیدوکائین ، فنی توئین و وارفارین مشاهده نشده است. نازاتیدین سیستم آنزیمی متابولیزه کننده دارو مرتبط با سیتوکروم P-450 را مهار نمی کند. بنابراین انتظار نمی رود که تداخلات دارویی با واسطه مهار متابولیسم کبدی رخ دهد. در بیمارانی که روزانه دوزهای بسیار زیاد (3900 میلی گرم) آسپرین تجویز می شود ، افزایش همزمان سطح سالیسیلات سرم هنگام مصرف همزمان نیژاتیدین ، 150 میلی گرم در سال ، مشاهده شد.
سرطان زایی ، جهش زایی ، اختلال در باروری – یک مطالعه 2 ساله سرطان زایی خوراکی در موش صحرایی با دوزهای بالای 500 میلی گرم در کیلوگرم در روز (حدود 13 برابر دوز توصیه شده انسانی براساس سطح بدن) هیچ مدرکی از اثر سرطان زا نشان نداد. یک افزایش مرتبط با دوز در تراکم سلولهای شبه آنتروکرومافین (ECL) در مخاط اکسینتیک معده مشاهده شد. در یک مطالعه 2 ساله روی موش ها ، هیچ شواهدی از اثر سرطان زا در موش های نر وجود نداشت. گرچه گره های پلاستیک کبد در مردان با دوز بالا در مقایسه با دارونما افزایش یافته است. Female mice given the high dose of nizatidine (2,000 mg/kg/day, about 27 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) showed marginally statistically significant increases in hepatic carcinoma and hepatic nodular hyperplasia with no numerical increase seen in any of the other dose groups. The rate of hepatic carcinoma in the high-dose animals was within the historical control limits seen for the strain of mice used. The female mice were given a dose larger than the maximum tolerated dose, as indicated by excessive (30%) weight decrement as compared with concurrent controls and evidence of mild liver injury (transaminase elevations). The occurrence of a marginal finding at high dose only in animals given an excessive and somewhat hepatotoxic dose, with no evidence of a carcinogenic effect in rats, male mice, and female mice (given up to 360 mg/kg/day, about 5 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area), and a negative mutagenicity battery are not considered evidence of a carcinogenic potential for nizatidine.
Nizatidine was not mutagenic in a battery of tests performed to evaluate its potential genetic toxicity, including bacterial mutation tests, unscheduled DNA synthesis, sister chromatid exchange, mouse lymphoma assay, chromosome aberration tests, and a micronucleus test.
In a 2-generation, perinatal and postnatal fertility study in rats, doses of nizatidine up to 650 mg/kg/day (about 17.5 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) produced no adverse effects on the reproductive performance of parental animals or their progeny.
Pregnancy—Teratogenic Effects—Pregnancy Category B— Oral reproduction studies in pregnant rats at doses up to 1500 mg/kg/day (about 40.5 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) and in pregnant rabbits at doses up to 275 mg/kg/day (about 14.6 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to nizatidine. با این حال ، هیچ مطالعه کافی و کنترل شده ای روی زنان باردار وجود ندارد. از آنجا که مطالعات تولید مثل روی حیوانات همیشه پیش بینی کننده پاسخ انسان نیستند ، این دارو فقط در صورت نیاز واضح در دوران بارداری باید استفاده شود.
Nursing Mothers—Studies conducted in lactating women have shown that 0.1% of the administered oral dose of nizatidine is secreted in human milk in proportion to plasma concentrations. Because of the growth depression in pups reared by lactating rats treated with nizatidine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use— Effectiveness in pediatric patients DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION)
Clinical Trials (Pediatric). In randomized studies, nizatidine was administered to pediatric patients for up to eight weeks, using age appropriate formulations. A total of 230 pediatric patients from 2 to 18 years of age were administered nizatidine at a dose of either 2.5 mg/kg b.i.d, or 5.0 mg/kg b.i.d, (patients 12 years and under) or 150 mg b.i.d (12 to 18 years). Patients were required to have either symptomatic, clinically suspected or endoscopically diagnosed GERD with age-relevant symptoms. In patients 2 to 18 years of age, nizatidine was found generally safe and well-tolerated. In these studies in patients 12 years and older, nizatidine was found to reduce the severity and frequency of GERD symptoms, improve physical well-being, and reduce the frequency of supplemental antacid consumption. No efficacy in pediatric patients
Geriatric Use— Of the 955 patients in clinical studies who were treated with nizatidine, 337 (35.3%) were 65 and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these and younger subjects. سایر تجربیات بالینی گزارش شده تفاوت در پاسخ های بین افراد مسن و بیماران جوان را مشخص نکرده است ، اما حساسیت بیشتر برخی از افراد مسن را نمی توان رد کرد.
شناخته شده است که این دارو به طور قابل توجهی از طریق کلیه دفع می شود و خطر واکنش های سمی به این دارو ممکن است در بیمارانی که عملکرد کلیه آنها مختل است بیشتر باشد. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function (see Dosage and Administration).
Adverse Reactions in Adults
Worldwide, controlled clinical trials of nizatidine included over 6,000 patients given nizatidine in studies of varying durations. Placebo-controlled trials in the United States and Canada included over 2,600 patients given nizatidine and over 1,700 given placebo. Among the adverse events in these placebo-controlled trials, anemia (0.2% vs 0%) and urticaria (0.5% vs 0.1%) were significantly more common in the nizatidine group.
Incidence in Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials in the United States and Canada—Table 7 lists adverse events that occurred at a frequency of 1% or more among nizatidine-treated patients who participated in placebo-controlled trials. The cited figures provide some basis for estimating the relative contribution of drug and non-drug factors to the side-effect incidence rate in the population studied.
|
*Events reported by at least 1% of nizatidine-treated patients are included. |
|||||
| Percentage of Patients Reporting Event |
Percentage of Patients Reporting Event |
||||
| Body System/ Adverse Event* |
Nizatidine (N=2,694) |
Placebo (N=1,729) |
Body System/ Adverse Event* |
Nizatidine (N=2,694) |
Placebo (N=1,729) |
| Body as a Whole | Nervous | ||||
| Headache | 16.6 | 15.6 | Dizziness | 4.6 | 3.8 |
| Pain | 4.2 | 3.8 | Insomnia | 2.7 | 3.4 |
| Asthenia | 3.1 | 2.9 | Abnormal dreams | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Chest pain | 2.3 | 2.1 | Somnolence | 1.9 | 1.6 |
| Infection | 1.7 | 1.1 | Anxiety | 1.8 | 1.4 |
| Injury, accident | 1.2 | 0.9 | Nervousness | 1.1 | 0.8 |
| Digestive | Respiratory | ||||
| اسهال | 7.2 | 6.9 | Rhinitis | 9.8 | 9.6 |
| Dry mouth | 1.4 | 1.3 | Pharyngitis | 3.3 | 3.1 |
| Tooth disorder | 1.0 | 0.8 | Sinusitis | 2.4 | 2.1 |
| Musculoskeletal | Cough, increased | 2.0 | 2.0 | ||
| Myalgia | 1.7 | 1.5 | Skin and Appendages | ||
| Rash | 1.9 | 2.1 | |||
| Pruritis | 1.7 | 1.3 | |||
| Special Senses | |||||
| Amblyopia | 1.0 | 0.9 | |||
A variety of less common events were also reported; it was not possible to determine whether these were caused by nizatidine.
Hepatic—Hepatocellular injury, evidenced by elevated liver enzyme tests (SGOT [AST], SGPT [ALT], or alkaline phosphatase), occurred in some patients and was possibly or probably related to nizatidine. In some cases, there was marked elevation of SGOT, SGPT enzymes (greater than 500 IU/L) and, in a single instance, SGPT was greater than 2,000 IU/L. The overall rate of occurrences of elevated liver enzymes and elevations to 3 times the upper limit of normal, however, did not significantly differ from the rate of liver enzyme abnormalities in placebo-treated patients. All abnormalities were reversible after discontinuation of nizatidine. Since market introduction, hepatitis and jaundice have been reported. Rare cases of cholestatic or mixed hepatocellular and cholestatic injury with jaundice have been reported with reversal of the abnormalities after discontinuation of nizatidine.
Cardiovascular—In clinical pharmacology studies, short episodes of asymptomatic ventricular tachycardia occurred in 2 individuals administered nizatidine and in 3 untreated subjects.
CNS—Rare cases of reversible mental confusion have been reported.
Endocrine—Clinical pharmacology studies and controlled clinical trials showed no evidence of antiandrogenic activity due to nizatidine. Impotence and decreased libido were reported with similar frequency by patients who received nizatidine and by those given placebo. Rare reports of gynecomastia occurred.
Hematologic—Anemia was reported significantly more frequently in nizatidine- than in placebo-treated patients. Fatal thrombocytopenia was reported in a patient who was
treated with nizatidine and another H2-receptor antagonist. On previous occasions, this
patient had experienced thrombocytopenia while taking other drugs. Rare cases of thrombocytopenic purpura have been reported.
Integumental — Sweating and urticaria were reported significantly more frequently in nizatidine- than in placebo-treated patients. Rash and exfoliative dermatitis were also reported. Vasculitis has been reported rarely.
Hypersensitivity — As with other H2-receptor antagonists, rare cases of anaphylaxis following administration of nizatidine have been reported. Rare episodes of hypersensitivity reactions (eg, bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, rash, and eosinophilia) have been reported.
Body as a Whole—Serum sickness-like reactions have occurred rarely in conjunction with nizatidine use.
Genitourinary—Reports of impotence have occurred.
Other—Hyperuricemia unassociated with gout or nephrolithiasis was reported. Eosinophilia, fever, and nausea related to nizatidine administration have been reported.
Postmarketing
Respiratory—pneumonia
Adverse Reactions (Pediatric)
In controlled clinical trials in pediatric patients (age 2 to 18 years), nizatidine was found to be generally safe and well tolerated. The principal adverse experiences (> 5%) were pyrexia, nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, vomiting, irritability, nasal congestion and cough. Most adverse events were mild or moderate in severity. Mild elevations in serum transaminase (1-2 x ULN) were noted in some patients. One subject experienced a seizure by EEG diagnosis after taking Axid Oral Solution 2.5 mg/kg b.i.d. for 23 days. The adverse reactions reported for nizatidine may also occur with Axid Oral Solution.
بیش از حد مصرف
Overdoses of nizatidine have been reported rarely. The following is provided to serve as a guide should such an overdose be encountered.
Signs and Symptoms —There is little clinical experience with overdosage of nizatidine in humans. Test animals that received large doses of nizatidine have exhibited cholinergic-type effects, including lacrimation, salivation, emesis, miosis, and diarrhea. Single oral doses of 800 mg/kg in dogs and of 1,200 mg/kg in monkeys were not lethal. Intravenous median lethal doses in the rat and mouse were 301 mg/kg and 232 mg/kg respectively.
In the two 8-week pediatric exposure trials of nizatidine in 256 pediatric patients, there were no cases of deliberate overdosage. In one study of nizatidine 10 mg/kg/day, drug compliance rates up to 7.5% above 100% compliance were not associated with clinically significant adverse events.
Treatment—To obtain up-to-date information about the treatment of overdose, a good resource is your certified Regional Poison Control Center. Telephone numbers of certified Poison Control Centers are listed in the Physicians’ Desk Reference (PDR). در مدیریت مصرف بیش از حد ، احتمال مصرف بیش از حد دارو ، تداخل بین داروها و سینتیک دارویی غیرمعمول را در بیمار خود در نظر بگیرید.
If overdosage occurs, use of activated charcoal, emesis, or lavage should be considered along with clinical monitoring and supportive therapy. The ability of hemodialysis to remove nizatidine from the body has not been conclusively demonstrated; however, due to its large volume of distribution, nizatidine is not expected to be efficiently removed from the body by this method.
مقدار و نحوه مصرف:
Active Duodenal Ulcer —The recommended oral dosage for adults is 300 mg once daily at bedtime. An alternative dosage regimen is 150 mg twice daily.
Maintenance of Healed Duodenal Ulcer —The recommended oral dosage for adults is 150 mg once daily at bedtime.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease —The recommended oral dosage in adults for the treatment of erosions, ulcerations, and associated heartburn is 150 mg twice daily.
Active Benign Gastric Ulcer—The recommended oral dosage is 300 mg given either as 150 mg twice daily or 300 mg once daily at bedtime. Prior to treatment, care should be taken to exclude the possibility of malignant gastric ulceration.
Each mL of Axid Oral Solution contains 15 mg of nizatidine. In adults, Axid Oral Solution may be substituted for any of the above indications using equivalent doses of the oral solution.
Pediatric Dosing—Each mL of oral solution contains 15 mg of nizatidine. Axid Oral Solution is indicated for pediatric patients 12 years of age or older. For pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, the dosage of nizatidine is 150 mg b.i.d. (2 tsp, b.i.d.)
The following dosage recommendations are provided:
Erosive Esophagitis—For pediatric patients 12 years or older, the dosage is 150 mg b.i.d. (300 mg/d). The maximum daily dose for nizatidine PO is 300 mg/d. The dosing duration may be up to eight weeks.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease—For pediatric patients 12 years or older, the dosage is 150 mg b.i.d. (300 mg/d). The maximum daily dose for nizatidine PO is 300 mg/d. The dosing duration may be up to eight weeks.
Dosage Adjustment for Patients With Moderate to Severe Renal Insufficiency —The dose for patients with renal dysfunction should be reduced as follows:
| Active Duodenal Ulcer, GERD, and Benign Gastric Ulcer | |
| Creatine Clearance | Dose |
| 20-50 mL/min | 150 mg daily |
| 150 mg every other day | |
| Maintenance Therapy | |
| Creatine Clearance | Dose |
| 20-50 mL/min | 150 mg every other day |
| 150 mg every 3 days | |
Some elderly patients may have creatinine clearances of less than 50 mL/min, and, based on pharmacokinetic data in patients with renal impairment, the dose for such patients should be reduced accordingly. The clinical effects of this dosage reduction in patients with renal failure have not been evaluated.
Based on the pharmacokinetic data in elderly patients with renal impairment, pediatric patients with creatinine clearances less than 50 mL/min should have their dose of nizatidine reduced accordingly. The clinical effects of this dose reduction in pediatric patients with renal failure have not been evaluated.
نحوه تهیه
Axid (nizatidine) Oral Solution 15 mg/mL is formulated as a clear, yellow, oral solution with bubble gum flavor, available as:
Bottles of 480 mL (16 fl. oz.) – NDC# 52268-147-62
در دمای 25 درجه سانتیگراد (77 درجه فارنهایت) نگهداری شود. excursions permitted to 15° – 30°C (59° – 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] and dispense in tight, light-resistant container.
ساخته شده برای:
Braintree Laboratories, Inc.
Braintree, MA 02185
By:
Lyne Laboratories, Inc.
Brockton, MA 02301, USA
Address Medical Inquiries to:
Braintree Laboratories, Inc.
Medical Affairs
P.O. Box 850929 Braintree, MA 02185
PRINTED IN USA 7/08
©2005 Braintree Laboratories, Inc.
Principal Display Panel – 15mg Bottle Label
NDC 52268-147-62
Axid®
(nizatidine)
Oral Solution
15 mg/mL
480 mL
Rx only
Braintree Laboratories Inc

| AXID nizatidine solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler – Braintree Laboratories, Inc. (107904591) |
- Prescribing Information
- Nizatidine Solution (FDA)
- Other brands
- Axid
سایر فرمول بندی ها
- Axid AR
















نظرات کاربران